💻 프로그래밍 언어/C++
C++ 6주차
SA성아
2023. 10. 18. 12:46
구조체
struct Man {
int age;
double weight;
};
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
Man lee;
lee.age = 40;
lee.weight = 70;
std::cout << lee.age << " " << lee.weight << std::endl;
}구조체: C vs C++

멤버의 접근 속성 클래스와 객체 만들기
정수(Integer) 클래스와 객체

클래스 멤버의 접근 권한

Access modifiers

클래스 멤버의 접근 권한 : private(전용)

클래스 멤버의 접근 권한: public(범용)

클래스 멤버의 접근 권한: protected(보호)

class
class Man {
private:
int age;
double weight;
public:
int getAge() {
return age;
}
void setAge(int a) {
age = a;
}
double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
void setWeight(double w) {
weight = w;
}
};
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
Man lee;
//lee.age = 40; //error C2248: 'Man::age': private 멤버('Man' 클래스에서 선언)에 액세스할 수 없습니다.
lee.setAge(40);
//lee.weight = 70;
lee.setWeight(70.2);
std::cout << lee.getAge() << " " << lee.getWeight() << std::endl;
}멤버함수를 클래스 안에서 정의
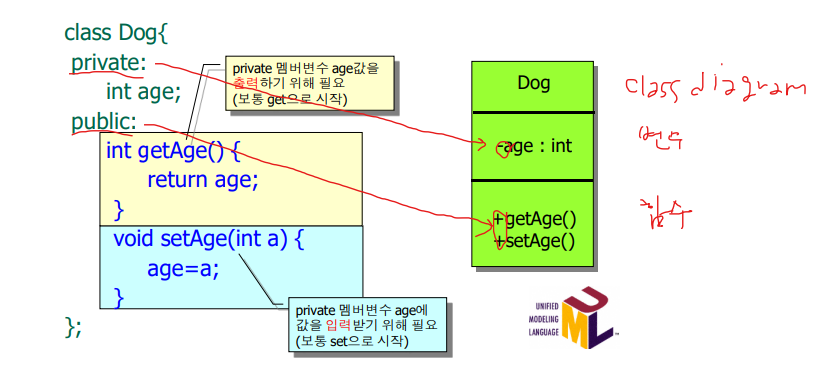
class diagram

함수 정의, 호출, 선언

범위 지정 연산자(scope resolution operator) '::'

using과 namespace
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//네임스페이스로 std 사용, 잘 쓰지 않음
int main()
{
cout<<"소프트웨어"<<endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using std::cout; //더 좋은 방법
using std::endl;
//이제부터 cout은 std::cout을 참조하겠다!
int main()
{
cout<<"소프트웨어"<<endl;
return 0;
}
C++: namespace
namespace는 코드의 일부를 그룹화하는 방법으로 프로그램에서 동일한 이름을 가진 여러 항목이 있을 때, 그들이 서로 충돌하지 않도록 하는데 도움이 된다.
ex)
두 개의 'add' 함수가 있다고 생각해보세요. 하나는 'Math'라는 namespace에 있고 다른 하나는 'Physics'라는 namespace에 있습니다.
namespace Math {
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
}
namespace Physics {
int add(int a, int b) {
return 2 * (a + b);
}
}이제 'Math::add'와 'Physics::add' 두 함수는 완전히 다르게 취급됩니다. 따라서 이름 충돌 없이 같은 이름의 함수를 사용할 수 있습니다.
int main() {
cout << Math::add(2, 3); // 출력: 5
cout << Physics::add(2, 3); // 출력: 10
return 0;
}즉, namespace는 코드를 조직화하고 식별자(함수명, 변수명 등) 간의 충돌을 방지하는 역할을 합니다.
namespace
namespace AA
{
int add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
}//헤더파일namespace BB
{
int add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y + 1;
}
}
//헤더파일#include <iostream>
#include "aa.h"
#include "bb.h"
int add(int x, int y) { return x + y + 2; }
int main()
{
std::cout << AA::add(1, 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << BB::add(1, 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << add(1, 2);//전역 namespace
return 0;
}std namespace

inline
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
#define sum(i, j) i + j // 매크로함수
inline int iSum
(int i, int j) // inline 함수
{
return i + j;
}
int add(int i, int j) // 일반 함수
{
return i + j;
}
int main() {
cout << sum(10, 20) /2 << ","; //10+20/2, 매크로함수의 부작용
cout <<iSum(10, 20) /2 << ","; //(10+20) /2
cout << add(10, 20) /2; //(10+20) /2
return 0;
}장점: 시간 절약
단점: 여러 번 호출하면 파일 사이즈가 커짐
자동 inline 함수

실습 3 -2: 객체의 멤버 호출
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
int getAge();
void setAge(int a);
};
int Dog::getAge() {
return age;
}
void Dog::setAge(int a) {
age = a;
}
int main() {
Dog happy; //Dog class의 happy 객체 정의
happy.setAge(3); //2.age는 private멤버로 클래스 밖에서 접근 불가
cout << happy.getAge(); //3. age는 전용멤버로 접근 불가
return 0;
}출처: C++ 프로그래밍 강의 자료
